Why We Looked Into This »?👀
|
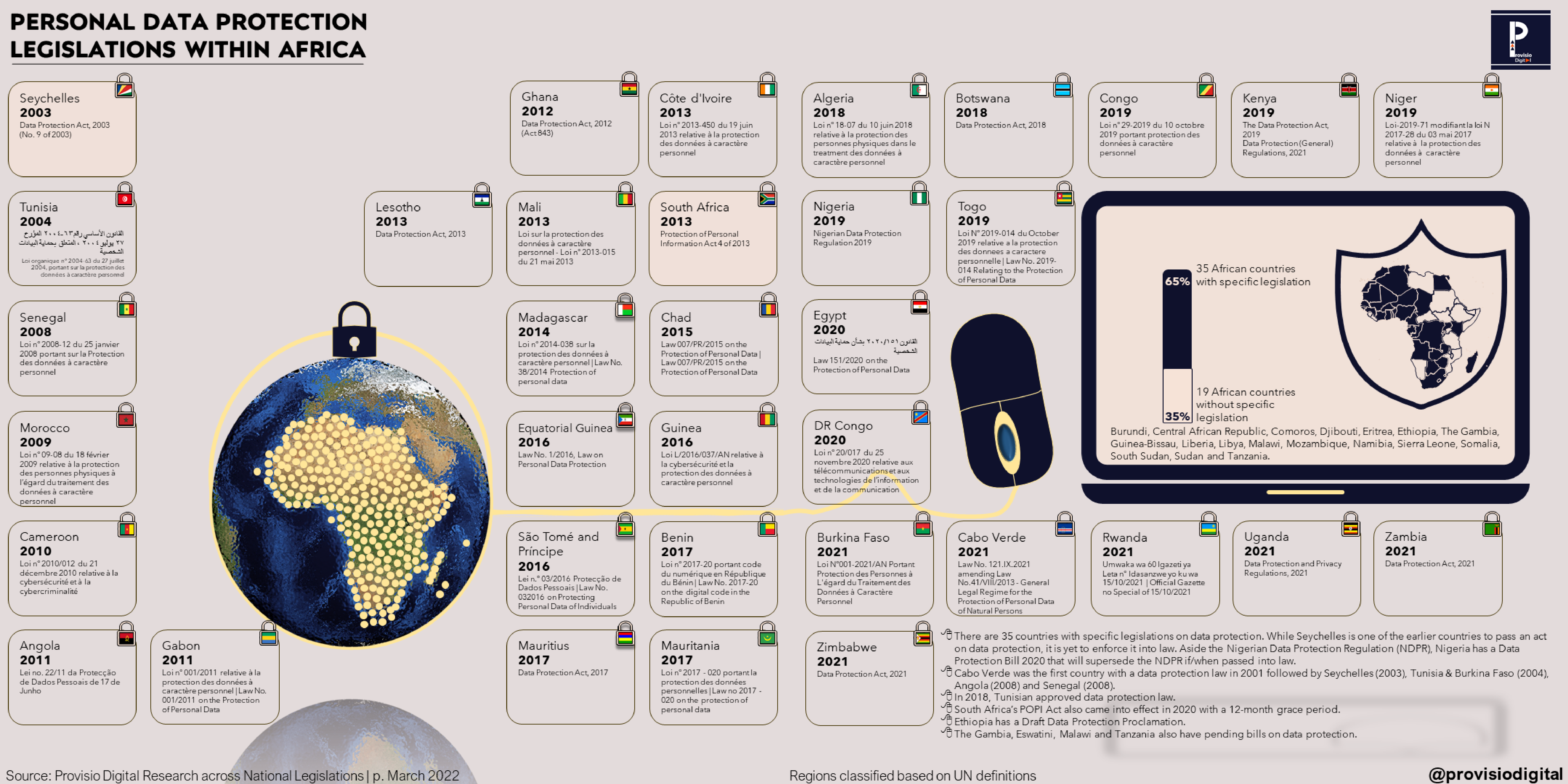
Personal Data Protection Legislations in Africa
- For the past twenty years, African countries have passed laws and regulations on the usage data protection. This involves the collection, treatment, transmission, storage, and use of personal data by persons, the government, local authorities, and legal persons, as well as automated processing and non-automated processing of personal data contained in files, or processing of data for different uses.
- Whereas the constitutions may make provisions on the protection of citizens’ data and privacy, the advent of social media, e-commerce and internet of things, has made countries with existing data protection laws modify existing laws and those without any specific laws expand on the specificity of the use of citizens’ data. .
- Cabo Verde (Cape Verde) was the first African country to pass such laws in 2001 with ‘Regime Jurídico Geral de Protecção de Dados Pessoais a Pessoas Singulares Lei n° 133/V/2001 of 22 January 2001’. Seychelles (2003), Tunisia & Burkina Faso (2004), Angola (2008) and Senegal (2008) are others who followed suit..
- To date, 35 countries have data protection laws and/or regulations. Most of the countries without these laws are in East Africa
- Countries with pending bills on data protection include The Gambia, Eswatini, Nigeria, Malawi and Tanzania.
- Some countries have witnessed issues with biometric data and storage alongside national IDs.
To download the PDF version of this piece, click the link below:
Data Privacy Laws Full Spread – @provisiodigital
View this post on Instagram

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.


